Tooth infections are far more dangerous than most people realize. They can spread to the bloodstream if left untreated, resulting in serious problems. In this blog article, we will look at how tooth infections develop, the risks of them spreading to the blood, and the actions you may take to detect and treat them early.
Understanding Tooth Infections
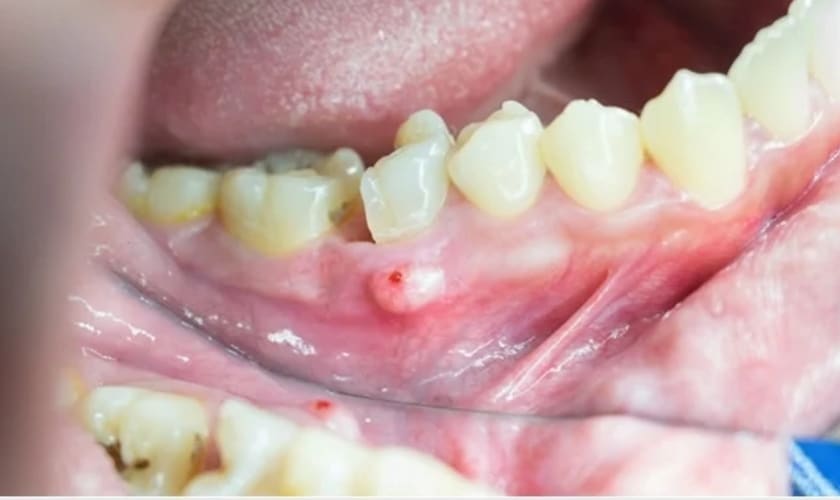
A tooth infection, commonly known as a dental abscess, develops when bacteria infiltrate and infect the pulp of a tooth. Dental decay, damaged teeth, or gum disease usually cause this. The infection can spread and cause pus to accumulate, resulting in discomfort, swelling, and redness in the afflicted region. If left untreated, tooth infections can cause a range of problems. These include the creation of an abscess, which is a pocket of pus that occurs at the root of the tooth, as well as the infection spreading to adjacent tissues such as the gums or jawbone. The infection can enter the circulation and produce systemic problems in extreme situations.
Potential Consequences Of A Tooth Infection Spreading To The Blood
Sepsis can occur when a dental infection spreads to the bloodstream. Sepsis is a potentially fatal illness that can affect various organs and systems throughout the body. It can cause symptoms including fever, chills, a racing heart, low blood pressure, disorientation, and difficulty breathing. The risks of a tooth infection spreading to the bloodstream should not be underestimated. Sepsis, if not treated swiftly, can result in organ failure, tissue damage, and even death. As a result, it is critical to recognize the symptoms and get medical assistance as soon as possible.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Tooth Infection Spreading To The Blood
It is critical to recognize the symptoms that may suggest that a tooth infection has migrated to the bloodstream. While this is not an entire list, some typical signs are as follows:
1. High fever: A fever that does not go away with over-the-counter treatment.
2. Rapid heart rate: A particularly quick heartbeat, even at rest.
3. Low blood pressure: The symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting episodes.
4. Confusion or mental changes: Difficulty concentrating, disorientation, or behavioral changes.
5. Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, fast breathing, or feeling out of breath. If you have a tooth infection and experience symptoms, you mustn’t disregard them. Immediate medical intervention is required for accurate evaluation and treatment.
Seeking Professional Help And Diagnosis
If you feel that a tooth infection has migrated to your circulatory system, you should see an oral surgeon or medical professional at once. They will examine you thoroughly and may request diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of an infection in your bloodstream. Blood tests to look for an increased white blood cell count, which indicates an infection or blood cultures to identify the specific bacteria causing the illness are common diagnostic procedures. Imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans may be suggested in some circumstances to determine the level of the illness.
Treatment Options And Prevention
Here is an overview of the treatment approaches commonly used to address both tooth infections and blood infections:
1. Antibiotics: In treating a bacterial bloodstream infection, healthcare providers administer carefully selected intravenous antibiotics based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and its sensitivity to various antibiotics.
2. Drainage of abscesses: When an infection develops at the root of a tooth, it may require draining to eliminate pus and relieve pressure. This can be achieved through a small incision or a root canal operation.
3. Root canal treatment or extraction: Once the infection has been controlled, the dentist will examine the impacted tooth to decide the best treatment. Sometimes, a root canal may be recommended to remove the infected pulp, clean the root canal system, and seal the tooth.
If the infection has inflicted substantial damage or if it is impossible to salvage the tooth, the dentist may need to perform an extraction.
Preventing dental infections from spreading to the bloodstream is always preferable to curing them.
Here are some pointers to help you reduce your risk:
1. Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and also clean your teeth with dental floss or interdental brushes. Visit your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups.
2. Treat dental issues promptly: If you find any signs of tooth decay, gum disease, or cracked teeth, visit your dentist as soon as possible. Early action can stop the illness from spreading and developing.
3. Practice healthy habits: Avoid smoking, alcohol consumption, and sugar-content foods and drinks, as they can cause tooth decay and damage your natural immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
4. Use protective gear: If you participate in activities that may endanger your teeth, such as contact sports, you must wear a mouthguard to protect your teeth from trauma.
5. Practice mindful eating: Consider what you consume and how it may affect your dental health. To maintain strong teeth and gums, eat a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats.
First, finding the signs of a tooth infection spreading to the blood is crucial for timely intervention. Awareness is essential for comprehending tooth infections and their possible repercussions, as well as identifying the signs that require quick care. Seeking expert assistance and receiving an accurate diagnosis are critical in establishing the best treatment strategy.
Remember to prioritize your oral health by receiving regular dental treatment and addressing any dental concerns as soon as possible. You may dramatically lower the chance of dental infections spreading to the blood by practicing proper oral hygiene, seeking prompt treatment, and adopting healthy behaviors. Your dentist is your partner in keeping your mouth healthy and preventing issues, so don’t be afraid to contact them if you detect any complications or have any worries.